Introduction
Let’s face it. It is crucial to prevent computer systems from overheating. Excessive heat can significantly reduce the system’s performance. The heat may even damage the system and render it useless. How can we dissipate the heat to keep the computer systems’ performance intact? We use heatsinks. In this post, we will discuss heatsinks from inside and out. By the end, you will have enough knowledge to prevent your computing devices from excessive heat. So, let’s get started!

What is a heatsink?
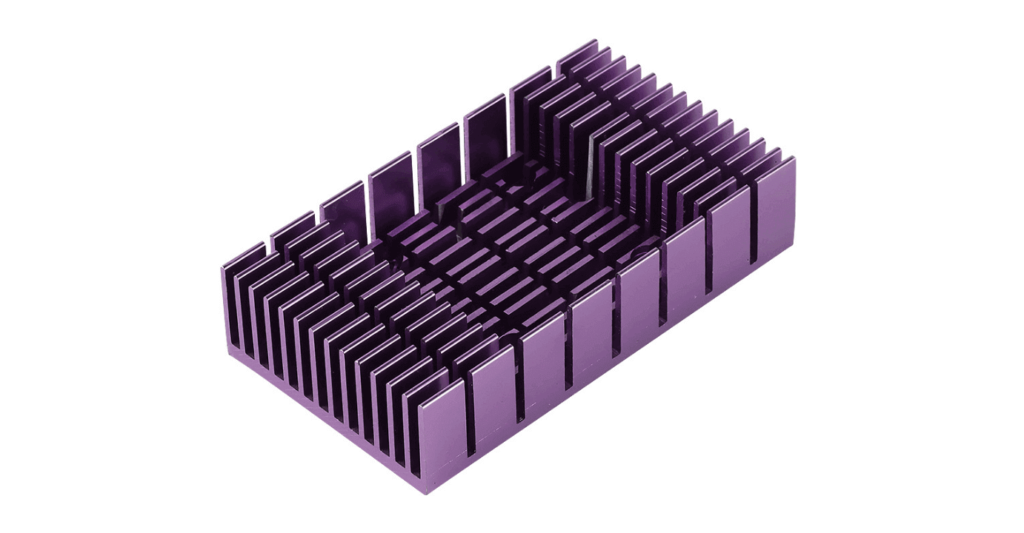
Let’s define heatsinks, shall we? Heatsinks are a type of passive heat exchanger that helps regulate the temperature of an electronic or mechanical device. The idea is to transfer the heat from a component generating it away from the device. Heatsinks have thermal conductors that take heat away from a heat-generating source. The heat is treated with the cooling medium on a large surface area.
How do heatsinks work?
Heatsinks are exceptional heat absorbers. They absorb heat from the component to which they are attached. You might have seen a rectangular-shaped metal component in the GPU or CPU unit. It is what draws heat away from the computing units. Heatsinks have fins where the heat transfers. The heat is finally released using a fan. You will find that the fans are attached to the heatsink to enable adequate air circulation. Since the fans run in reverse, they pull the hot air away from the CPU. That’s pretty much how heatsinks function.
But, are heatsinks really important? Well, they are. A CPU or GPU unit that runs without a heatsink will have to fight temperatures rising to dangerous levels. There’s a misconception running around in the electronics community that you need heatsinks only when you overclock your computer. Indeed, overclocking will produce an immense amount of heat. But CPUs and GPUs, in general, produce enough heat to damage the computer system.

What are the different types of heatsinks?
Now that you know why heatsinks are important, it’s time we discuss some of the crucial types of heatsinks. Most heatsinks are made of aluminum alloys or copper. The material used in the heatsinks depends on the application, heat intensity, heatsink production method, and budget. Although aluminum has lower thermal conductivity than copper, you will find it on most heatsinks as it is more cost-effective. Let’s discuss some essential aluminum heatsinks.
1.Stamped heatsinks
In this, the metal is stamped to create heatsinks. It uses a stamping machine which makes stamped heatsinks cheaper than extruded heatsinks. Such heatsinks are used for low-power applications.
2.Machining heatsinks
These heatsinks are produced using the machining process. Gangsaw is used to make inter fins with precision. Since blocks of material are removed during the process, a lot of metal might go to waste. Machining heatsinks are expensive as well.
3.Bonded-fin heatsinks
These heatsinks have individual metal fins bonded to the base of the component. We generally use thermal epoxy for the bond as it is economical.
4.Folded-fin heatsinks
Folded-fin heatsinks are high-performance heatsinks and have a large surface area. They have a very high heat-flux density, and it is quite expensive to set them up.
5.Skived heatsinks
Made using a skiving process, these heatsinks have very fine blocks of metal. We generally use copper to make skived heatsinks. These come in medium to high-performance heatsinks.
6.Forged heatsinks
Forged heatsinks, as the name suggests, are produced using compressive forces. In this, metals like copper and aluminum are forged into a heatsink.
7.Single fin assembly heatsinks
Do you need to install heatsinks in tight spaces? Use single fin assembly heatsinks. These have low to medium capacity and can be used for many applications. However, single fin assembly heatsinks are quite expensive.
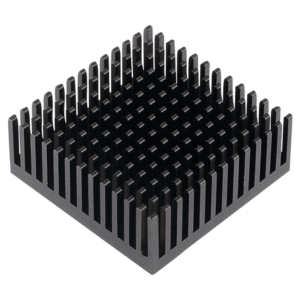
Factors responsible for heatsink performance
There are several parameters that you should consider when determining the performance of a heatsink. Factors like heatsink geometry, material, surface treatment, air velocity, and interface with device help figure out the suitable heatsink for any application.
While many of these parameters are quite standard, you should pay extra attention to how a heatsink interfaces with your device. Frankly speaking, most of the heatsink surfaces are quite rough. This is despite being manufactured to be flat and smooth.
As a result, the heatsink surface comes in contact with the component at very few points. The formation of air gaps leads to a significant drop in thermal conductivity. This is one reason why we use thermal interface material or TIM at the base of the heatsink. TIM helps fill these gaps and ensures proper heat conductivity between the device and the heatsink.
You should also check the thermal resistance of the heatsinks before using them. Thermal resistance is essentially the difference in temperature between the device surface and the air surrounding the heatsink.
Keep reading!
That’s all there is to know about heatsinks. This post is aimed at sharing information that will make you well-acquainted with how heatsinks work. Heatsinks are critical to ensure that the electrical components in any system work efficiently and produce high performance. The information mentioned above will help you choose a suitable heatsink for your application. Did you find this post useful? Don’t forget to check out other informative posts on the blog!